01
The
aRki-fighting
My E-Portfolio

THE
ARKI-
FIGHTING
connect with Me
ABOUT ME
Hi, my name is Shane Karla E. Barce of BSA-1C and this is my E-Portfolio for History of Architecture. This Portfolio serves as a reflection of everything I’ve learned and discovered as a first year student at Bicol State College of Applied Sciences and Technology.
History of Architecture is the study of how architecture has changed through the ages and in a variety of settings and civilizations.
With the use of certain techniques and, most importantly, imagination, architectural design aims to address and meet the demands for the creation of livable spaces.
02
THE ARKI-FIGHTING CONTENT:
Comparative table of architectural styles and the six(6) Influential factors
of Architectures
The Architectural Timeline
Top ten(10) Architectural Terms
Accomplished Classwork Outputs
Summary
References
03
COMPARATIVE TABLE OF ARCHITECTURAL STYLES AND THE SIX (6) INFLUENTIAL FACTORS OF ARCHITECTURE
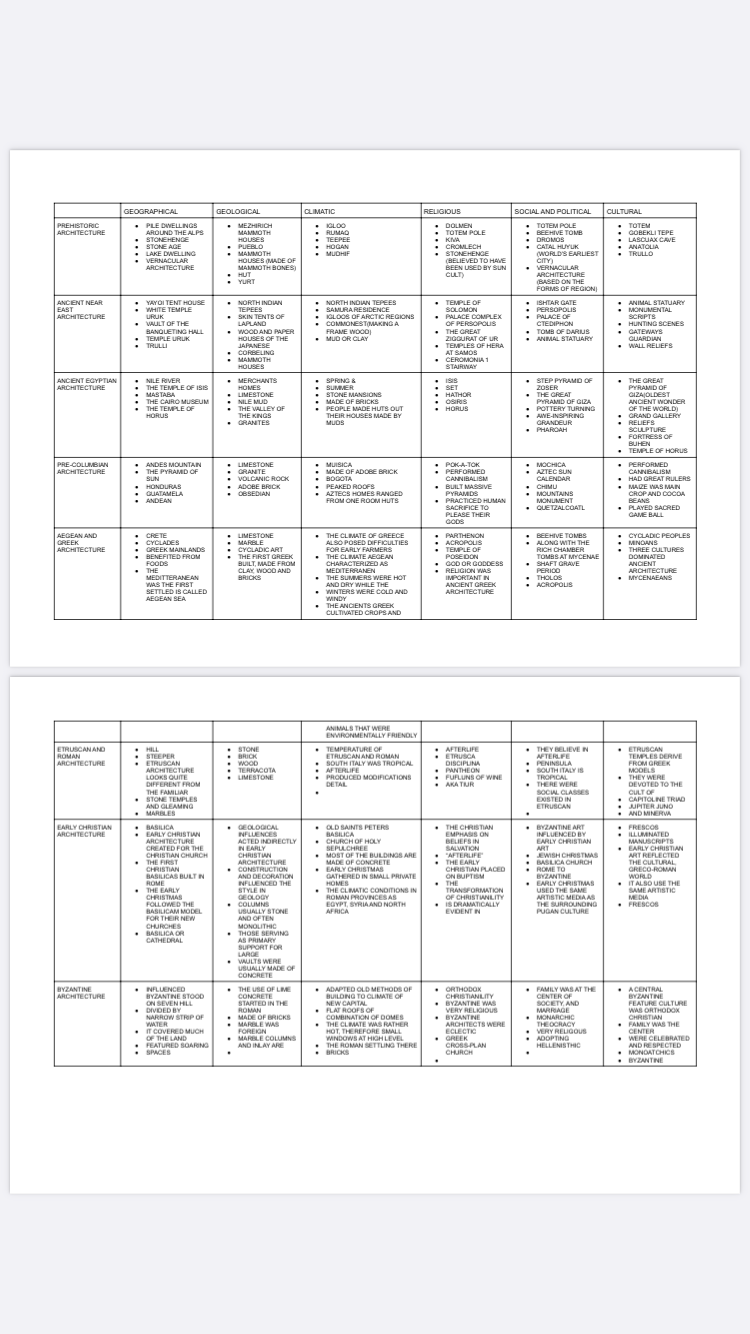
04
06
THE ARCHITECTURAL TIMELINE
• ANCIENT EGYPTIAN HISTORY
4500 BC
AROUND 4500BC,SAILS WERE USED ON EGYPTIAN SHIPS FOR THE FIRST TIME. BOATS WERE THE MAIN FORM OF TRANSPORT IN ANCIENT EGYPT.
5000 BC
AROUND 5000BC MANY EGYPTIANS FARMED SHEEP AND CATTLE. SOME EGYPTIANS GREW WHEAT AND BARLEY ON THE FERTILE LAND PN THE NILE VALLEY.
6000 BC
IN 6000BC EARLY PEOPLE SETTLED IN THE NILE VALLEY. EGYPTIANS BEGIN TO USE CLAY AND SILT FROM THE RIVER TO MAKE POTTERY VESSELS.
3500 BC
AROUND 3500BC, CRAFTSMEN BEGAN TO CREATE THE FIRST WALL PAINTINGS USING HIEROGLYPHIC SYMBOLS IN THE EGYPTIAN WRITING SYSTEM.
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
3000BC
AROUND 3000BC,WALLED TOWNS AND VILLAGE WERE BUILT IN EGYPT. THE FIRST BUILDING WERE MADE OF MUD BRICK.
2500BC
AROUND 2500BC, EGYPTIANS BUI THE GREAT SPHINX AND THE GREAT PYRAMID AT GIZA . 2500BC-2000BC WAS THE OLD KINGDOM PERIOD.
1550BC
IT WAS AROUND 1550BC THAT MANY OF THE ROYAL TOMBS WERE BUILT IN THE VALLEY OF THE KINGS. 1550BC-332BC WAS THE PERIOD OF NEW KINGDOM.
1325 BC
KING TUTANKHAMUN WAS BURRIED IN THE VALLEY OF THE KINGS, IN 1992 HIS TOMB WAS DISCOVERE, INSIDE WERE WONDERFUL TREASURES AND THE MUMMU OF THE PHARAOH COVERED BY A BEAUTIFUL GOLD DEATH MASK.
332 BC
EGYPT WAS INVADED BY ALEXANDER THE GREAT WAS THEN RULED BY GREEK KINGS. THE ERA OF THE NEW KINGDOM ENDS.
• PREHISTORIC (STONE AGE) TIMELINE
07
1,600,000 BC
EARLY HUMAN START HUNTING USING SPEARS.
40,000 BC
EARLY HUMANS PAINT PICTURE IN CAVES IN SPAIN.
6,000 BC
GREAT BRITAIN BECOMES AN ISLAND.
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
2,000,000 BC
FIRST EARLY HUMANS
650,000 BC
EARLY HUMANS START TO USE HAND AXES.
12,000 BC
THE LAST WOOLLY MAMMOTH IN BRITAIN DIES.
3,000 BC
STONEHENGE IS STARTED.
Top Ten (10) Architectural Terms
08
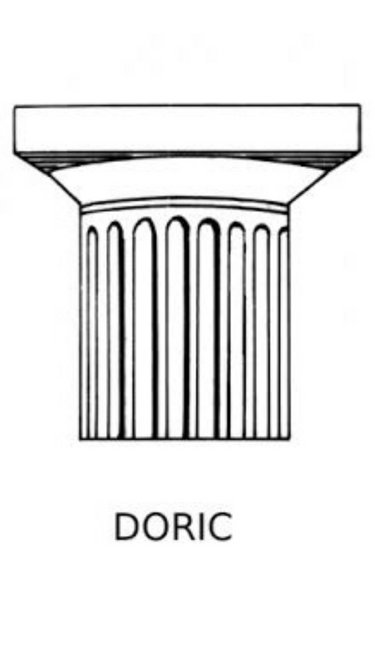
- doric
There are three classical orders in Ancient Greek and Roman architecture, and the Doric order is one of them.
It was created first and is the simplest of the three orders.
The decoration on the column heads makes it simplest to identify between the orders.
Here, there isn't much embellishment on the column head.
2. Ionic
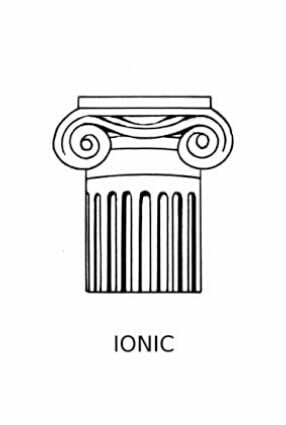
The Ionic order is one of three classical orders in Ancient Greek and Roman architecture. It is the second order to be developed and is the middle ground in terms of ornamentation.
3. corinthian
The Corinthian order is one of three classical orders in Ancient Greek and Roman architecture. It is the most elaborate of all three orders and was the last developed. The orders are easiest to distinguish by the ornamentation found in the column heads.

09
4. DOME
A DOME IS A STRUCTURAL SYSTEM IN THE FORM OF A HALF SPHERE THAT COMES FROM A SIMPLE ARCH. DOMES CAN BE MADE IN MANY SIZES AMD FORM MANY MATERIALS. THEY ARE MAJOR FEATURES IN COUNTLESS ARCHITECTURAL WORKS.
5. GROIN VAULT
A GROIN VAULT IS A TYPE OF VAULT ALSO KNOWN AS A DOUBLE BARREL VAULT OR A CROSS VAULT. IT IS CALLED A GROIN VAULT BECAUSE TWO BARREL VAULTS INTERSECT AND CREATE A GROIN EDGE.


10
6. KEYSTONE
THE KEYSTONE IS THE CENTER WEDGE-SHAPED PIECE OF MASONRY AT THE CENTER OF AN ARCH. OT KEEPS ALL THE OTHER PIECES IN PLACE AND HELPS TO KEEP THE ARCH STRUCTURALLY SOUND.
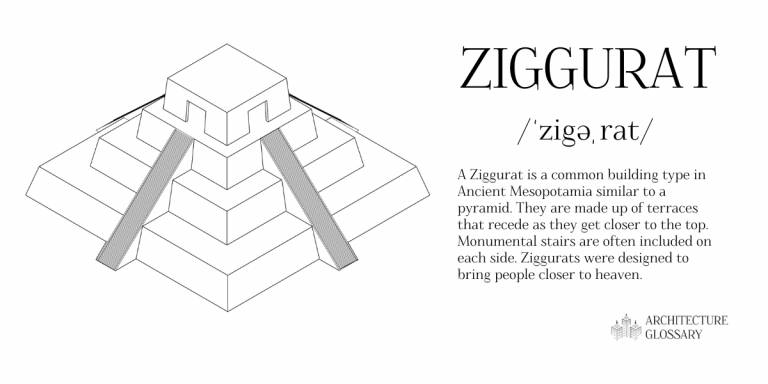
7. ZIGGURAT
A ZIGGURAT IS A COMMON BUILDING TYPE IN ANCIENT MESOPOTAMIA THAT IS SIMILAR TO A PYRAMID. ZIGGURATS ARE MADE UP OF TERRACES THAT RECEDE AS THEY GET CLOSER TO THE TOP. MONUMENTAL STAIRS ARE OFTEN INCLUDED ON EACH SIDE. ZIGGURATS WERE DESIGNED TO BRING PEOPLE CLOSER TO HEAVEN.

11
8. FLOOR PLAN
A FLOOR PLAN IS ONE OF THE MOST CRITICAL FORMS OF ARCHITECTURAL DRAWING. IT IS THE REPRESENTATION OF A WORK FROM ABOVE THAT CITS THROUGH WALLS TO SHOW THE CLEAREST REPRESENTATION OF ALL SPACES. MANY FLOOR PLAN ARE LABELED TO BEST SHOW THE FUNCTIONS OF EACH SPACE. ORHER COMMON DETAILS INCLUDE THE SWINGING DIRECTIONS OF DOORS, ENTRY, VERTICAL CIRCULATION, WALL THICKNESS THAT DESIGNATE MATERIAL, WINDOWS CUT OUTS, AND FURNITURE.
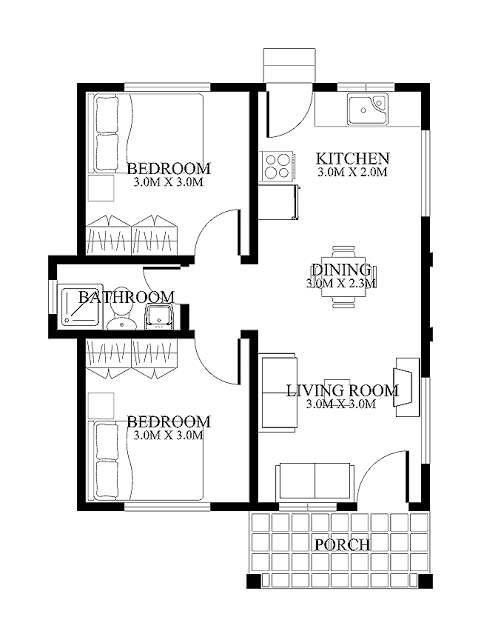
12
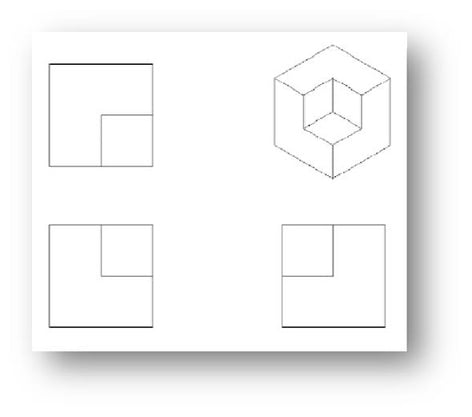
9. ISOMETRIC
ISOMETRIC ARE A FORM OF ARCHITECTURAL DRAWING THAT HELPS REPRESENT 3D OBJECTS IN 2D DRAWINGS. IT ALLOWS FOR AN EASILY UNDERSTANDABLE VIEW OF A SIMPLE PERSPECTIVE.
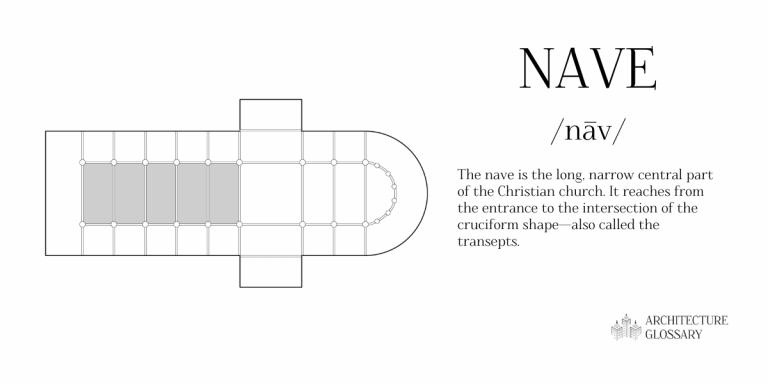
10. NAVE
THE NAVE IS THE LONG, NARROW CENTRAL PART OF THE CHRISTIAN CHURCH. IT REACHES FROM THE ENTRANCE TO THE INTERSECTION OF THE CRUCIFORM SHAPE-ALSO CALLED THE TRANSEPTS.
13
ACCOMPLISHED CLASSWORK OUTPUTS
14
In the task, The Factors that Influence the Architectur, the purpose of these factors is to guarantee the structural integrity of the structur. I’ve learned that these factors is important that architect should know.
In the task, The Ancient Egyptians Architectur, I’ve learned that the most important part in the Egyptian Architecture is the Mastabas. Mastabas are essential burial tombs primarily located on the bank of the river nile. The concept of building mastabas was greatly influenced by the construction of pyramids in ancient architectarchitecture.
In the task about tuscan order and doric order, the differences and similarities are both columns style is simple. Without carvings or ornament, however a tuscan order is traditionally more slender than a doric column.
ACCOMPLISHED CLASSWORK OUTPUTS
15
In the task about Aegean Architecture. Ancient Aegean Architecture was created primarily by three cultures and this are cycladic peoples, the minoans, and the mycenaeans.
In the task of Greek Architecture, I’ve discovered and learned that tall columns, meticulous detail, symmetr, harmon, and balance are all characteristics of greek architecture. The greeks created a wide variety of structures. The enormous temples that the greeks erected in honor of their gods are the primary surviving examples of greek architecture.
ACCOMPLISHED CLASSWORK OUTPUTS
Click down below
16
PREHISTORIC ARCHITECTURE
Prehistory basically covers the old stone age, middle stone age, and new stone age (Paleolithic, Mesolithic, Neolithic) periods, as well as portions of the bronze and iron ages.
11,600 BCE - 3,500 BCE
Prehistoric Architecture includes monumental structures such as stonehenge, cliff dwellings in the americas, and thatch and mud structures lost to time. The dawn of architecture is found in these structures.
17
ANCIENT NEAR EAST ARCHITECTURE
The ancient Near East was the home of early civilizations within a region roughly corresponding to the modern Middle East: Mesopotamia, ancient Egypt, ancient Iran, Anatolia/Asia Minor and the Armenian highlands, the Levant, Cyprus and the Arabian Peninsula.
Ishtar Gate
The Ancient Near East was an area of opposites, with dry deserts and lush river valleys, established civilizations and nomadic people, significant progress and intense warfare.
18
ANCIENT EGYPTIANS ARCHITECTURE
Egyptian architecture, which has been around since 3000 BC, is known for its huge walls covered in carvings of hieroglyphs and pictures, flat roofs, and buildings like the mastaba, obelisk, pylon, and the Pyramids.
Homes were constructed using baked bricks or clay.
The three most popular structures of ancient Egypt are probably the Great Pyramid at Giza A.K.A Pyramid of Khufu and the "Pyramid of Cheops"
19
PRE-COLUMBIAN ARCHITECTURE
Pre-Columbian” thus refers to the period in the Americas before the arrival of Columbus.
Mesoamerican Architecture
The majority of structures, especially those made of stone, were ornamented with ornamental iconography that showed animals, gods, and powerful monarchs.
Ancient Central and South American societies were skilled stone cutters and carvers as well, though they built more frequently from stucco and mud-brick than from timber.
20
AEGEAN AND GREEK ARCHITECTURE
TGreek architecture is known for tall columns, intricate detail, symmetry, harmony, and balance.
TThe architecture of ancient Greece has five trends - Dorian, Ionian, Corinthian, Tuscan, and composite.
Greek architects created the first three styles and have a strong influence on the other two. The architectural currents differ in their order - structure, arrangement.
21
ETRUSCAN AND ROMAN ARCHITECTURE
The development of Etruscan architecture took place between 900 and 27 BC, when it was finally absorbed by the burgeoning Roman civilisation.
The Etruscans were skilled builders of bridges, roads, houses, tombs, and city walls out of stone, wood, and other materials.
Roman Architecture Characteristics
Arches: Pont du Gard Aqueduct, featuring triple-tier arches to support the structure. Domes: The Pantheon, Rome, a temple dedicated to the Roman pantheon of gods. Columns: Temple of Portunus, Rome, which features columns in the Ionic style.
Roman
22
EARLY CHRISTIAN ARCHITECTURE
It might be either a straightforward hall, one split by columns into three longitudinal aisles, or enclosed on three sides by one- or two-story arcades with a dais on a short or long side.
Rome saw the construction of the first Christian basilicas, which were modified secular basilicas to suit the needs of the emerging religion.
Early Christian art and architecture adapted Roman artistic motifs and gave new meanings to what had been pagan symbols. Among the motifs adopted were the peacock, Vitis viniferavines, and the "Good Shepherd
23
BYZANTINE ARCHITECTURE
Byzantine structures featured soaring spaces and sumptuous decoration: marble columns and inlay, mosaics on the vaults, inlaid-stone pavements, and sometimes gold coffered ceilings.
Byzantine architecture is a style of building that flourished under the rule of Roman Emperor Justinian between A.D. 527 and 565. In addition to extensive use of interior mosaics, its defining characteristic is a heightened dome, the result of the latest sixth-century engineering techniques.
Hagia Sophia
24
Click on the link below

25